Age-old Symbols of Love and Affection 2023 Best Info
October 24, 2023
Breaking Down the Barriers to Remote Proctoring: Ensuring Fair and Secure Online Assessments
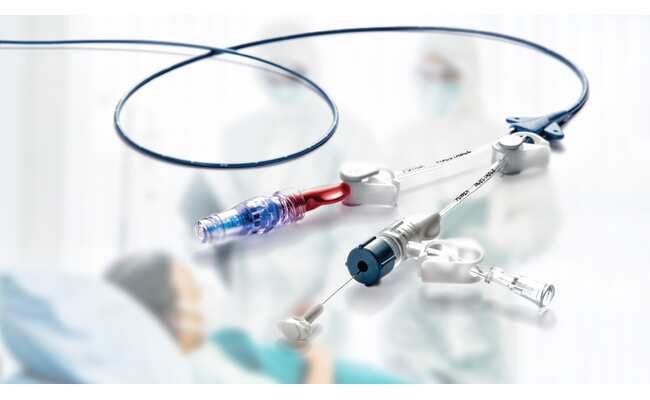
November 23, 2023Long-Term Vascular Access Devices and Their Impact on Healthcare is our today’s topic. In the dynamic landscape of modern healthcare, the need for effective and reliable vascular access cannot be overstated. For medical procedures such as chemotherapy and hemodialysis, the ability to access a patient’s vascular system over an extended period is crucial.
Long-term vascular access devices such as ports have emerged as indispensable tools in the healthcare armamentarium, providing a lifeline for patients requiring prolonged treatment.
According to the CFF, a port placed in your body provides recurring and long-term access to your bloodstream. It can be used to provide antibiotics, IV nutrition, and other intravenous fluids. When a port is implanted, no IV catheters, such as peripheral IVs or PICC lines, are required.
In this article, we will explore the significance of long-term vascular access devices and their far-reaching impact on healthcare.
Long-Term Vascular Access Devices And Their Impact on Healthcare

The Vital Role of Vascular Access Devices
Long-term vascular access devices serve as lifelines in the treatment of patients with chronic medical conditions. These devices are specifically designed to provide reliable and extended access to a patient’s bloodstream. This simplifies the administration of various medical interventions, such as medications, fluids, and other therapies.
Without these devices, the management of chronic illnesses and long-term therapies would be significantly more challenging. For example, in cancer treatment, chemotherapy regimens can extend over several months or years. Long-term vascular access devices, like central venous catheters, offer an efficient and safe way to administer these potent medications without repeated needle sticks.
Types of Long-Term Vascular Access Devices
Long-term vascular access devices come in various forms to cater to the diverse clinical needs of patients. Central venous catheters, commonly known as CVCs, are one of the most commonly used options. These are inserted into larger veins in the chest or neck and can stay in place for several weeks to months.
Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC lines) are another common choice. According to Cancer.Net, they’re inserted through a peripheral vein in the arm and advanced to a larger vessel, allowing for extended use. Additionally, implantable ports, placed beneath the skin and accessed via a needle, provide discreet and long-term access to the vascular system.
Benefits and Challenges
The advantages of long-term vascular access devices are evident, but they also come with a set of challenges. The benefits include the ability to reduce the number of needle sticks, decrease pain and discomfort, and ensure accurate and efficient administration of therapies.
However, these devices can be a potential source of infection, requiring stringent care and maintenance. Challenges also include the risk of complications such as clot formation, malposition, or dislodgement, which healthcare professionals must vigilantly monitor.
The Bard PowerPort Case
The Bard PowerPort is one case that serves as a stark example of the complexities and challenges associated with long-term vascular access devices. While these devices offer undeniable benefits, it is crucial to understand that they are not immune to risks. The Bard PowerPort, in particular, has faced significant scrutiny and legal action due to its complications.
The Bard PowerPort has been linked to a range of complications. This includes device fractures, migrations, infections, blood clots, embolisms, thrombosis, and, in the most tragic cases, patient fatalities. TorHoerman Law notes that several product liability lawsuits have been filed against the manufacturer and its subsidiaries as a consequence.
The legal actions allege that Bard marketed a device with known complications without addressing these issues adequately or providing adequate warnings to the public. Bard also attempted to shift blame onto healthcare providers, suggesting that device fractures occurred due to improper placement. However, internal company knowledge, brought to light through lawsuits, contradicted these claims.
According to an October 2023 update by Drugwatch, there is a notable absence of precise settlement figures in the Bard PowerPort litigation. This absence of a specific Bard Power Port lawsuit settlement amount can be attributed to the early stage of the legal proceedings. Matters such as this are intricate, and the complications involved necessitate a meticulous and comprehensive review of each case.
Improved Quality of Life
For patients requiring ongoing medical treatment, long-term vascular access devices significantly enhance their quality of life. These devices minimize the need for frequent venipunctures, which can be painful and distressing.
In particular, individuals with conditions like end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis benefit tremendously from reduced discomfort and increased convenience. Additionally, those with chronic conditions necessitating long-term intravenous treatments also experience significant benefits from these devices.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes
The impact of long-term vascular access devices on patient outcomes is profound. These devices ensure the consistent, precise delivery of necessary therapies. Patients with diabetes, for instance, who require insulin infusion can achieve better glycemic control.
Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy experience fewer complications, as the medications can be accurately administered, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and treatment interruptions. As a result, these devices contribute to improved clinical outcomes and better overall disease management.
The Economic Perspective
From an economic standpoint, long-term vascular access devices offer significant cost-saving benefits. By minimizing the need for frequent hospital admissions and outpatient visits, these devices reduce the financial burden on patients and healthcare systems.
Fewer complications and infections associated with venipunctures mean fewer resources are spent on treating avoidable medical issues, ultimately leading to cost reductions.
Ongoing Advancements and Future Prospects
The field of long-term vascular access devices continues to evolve. Advancements in materials and design are making devices more biocompatible and durable. Telemedicine and remote monitoring are being integrated into these devices, allowing healthcare providers to track patients’ conditions more closely.
Future prospects include the development of smart devices that can provide real-time data to improve patient care. This will make long-term vascular access devices even more patient-friendly and efficient. As technology continues to advance, these devices will remain at the forefront of modern medicine, ensuring patients receive the care they need.
Final Thoughts
Long-term vascular access devices are indispensable tools in modern healthcare, facilitating extended treatment for patients with chronic conditions. These devices simplify therapy administration, improve patient quality of life, enhance clinical outcomes, and offer economic advantages.
However, challenges, such as infection risk and device complications, underscore the importance of careful management. Recent legal cases, like the Bard PowerPort, serve as stark reminders of the need for robust device safety measures and transparency.
The future holds promising advancements in materials and technology, with smart devices and remote monitoring on the horizon. Long-term vascular access devices will remain vital, evolving to meet the ever-growing demand for effective, reliable, and patient-centered healthcare solutions.